Q1. What is detector? Draw the block diagram of a receiver of AM wave.
Solution
Detection or Demodulation is the process of retrieval of information from the modulated carrier wave at the receivers end . The device used for this purpose is called a detector or a demodulator.
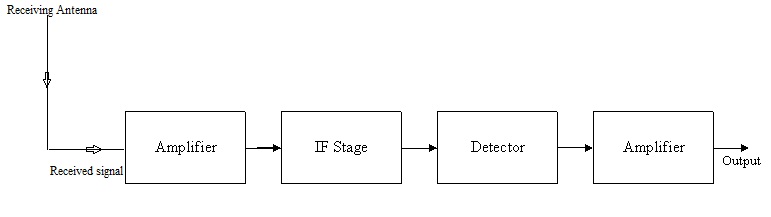 The block diagram of an AM wave receiver has been shown in the figure above. As the received signal from receiving antenna is a weak one, the signal is amplified by the use of an amplifier. To facilitate further processing, the carrier frequency is usually changed to a lower frequency by the use of an intermediate frequency stage (IF). After this the carrier is supplied to the detector. As the detected signal may not be strong enough to be made use of, we again amplify the detected modulating (message) signal before converting it into proper voice or video format.
The block diagram of an AM wave receiver has been shown in the figure above. As the received signal from receiving antenna is a weak one, the signal is amplified by the use of an amplifier. To facilitate further processing, the carrier frequency is usually changed to a lower frequency by the use of an intermediate frequency stage (IF). After this the carrier is supplied to the detector. As the detected signal may not be strong enough to be made use of, we again amplify the detected modulating (message) signal before converting it into proper voice or video format.
 The block diagram of an AM wave receiver has been shown in the figure above. As the received signal from receiving antenna is a weak one, the signal is amplified by the use of an amplifier. To facilitate further processing, the carrier frequency is usually changed to a lower frequency by the use of an intermediate frequency stage (IF). After this the carrier is supplied to the detector. As the detected signal may not be strong enough to be made use of, we again amplify the detected modulating (message) signal before converting it into proper voice or video format.
The block diagram of an AM wave receiver has been shown in the figure above. As the received signal from receiving antenna is a weak one, the signal is amplified by the use of an amplifier. To facilitate further processing, the carrier frequency is usually changed to a lower frequency by the use of an intermediate frequency stage (IF). After this the carrier is supplied to the detector. As the detected signal may not be strong enough to be made use of, we again amplify the detected modulating (message) signal before converting it into proper voice or video format.
Q2. Briefly explain the ground wave propagation of radio waves.
Solution
Radiowaves in medium band of radio broadcast are generally propagated in the form of ground waves (also known as the surface waves). These waves travel along the surface of earth. For ground wave transmission the transmitting antenna and receiving antenna are close to the surface of earth. Being of long wavelength (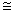 200 m or more), these waves can easily bend along with earth's surface and propagate.
While progressing along the surface of earth, the ground waves induces current in the ground and bends round the corner of the objects on earth.The energy of ground waves is gradually absorbed by earth and the power of these ground waves decrease with distance from the transmitting station.This phenomena of loss of power is called attenuation.The attenuation of ground waves increases rapidly with the increase in its frequency.
For ground wave propagation, the maximum coverage range depends upon : transmitting power and frequency of signal wave.The ground wave propagation is useful for low frequency signal waves , for short distances. Ground wave communication is not suited for high frequency signal wave and for long range communication.It is generally used for local broadcasting .
200 m or more), these waves can easily bend along with earth's surface and propagate.
While progressing along the surface of earth, the ground waves induces current in the ground and bends round the corner of the objects on earth.The energy of ground waves is gradually absorbed by earth and the power of these ground waves decrease with distance from the transmitting station.This phenomena of loss of power is called attenuation.The attenuation of ground waves increases rapidly with the increase in its frequency.
For ground wave propagation, the maximum coverage range depends upon : transmitting power and frequency of signal wave.The ground wave propagation is useful for low frequency signal waves , for short distances. Ground wave communication is not suited for high frequency signal wave and for long range communication.It is generally used for local broadcasting .
Q3. What is the importance of depth of modulation?
Solution
Modulation depth also referred as modulation index gives the quality and strength of the transmitted signal. If the modulation index is small, the extent of variation in the carrier amplitude will be small.Accordingly the audio signal being transmitted will not be strong.Greater the depth of modulation , clearer and stronger will be the audio signal.
Q4. Why do we need amplification of modulated signal in a transmitter and again need amplification before detection?
Solution
The power of the modulated signal is not high enough and hence the modulator is followed by a power amplifier. The amplifier provides necessary power and then feeds the modulated signal to the antenna of the transmitter.
While propagating through the channel. the transmitted signal gets attenuated.So to increase the power the receiving antenna is followed by an amplifier. The amplified signal is fed to the detector which separates the modulating signal and reproduces it back into message form.
Q5. Write main advantages and disadvantages of the AM technique.
Solution
Advantages of AM:
(i) Large coverage area is possible
(ii) Bandwidth required is comparatively small.
(iii) Technology and instruments needed for AM transmission and reception are comparatively simple and cheap.
Disadvantages of AM:
(i) Efficiency of AM transmitter is poor.
(ii) Noise content in reception is more.
(iii) There is interference due to adjacent channels and hence audio quality of reception is poor.
(iv) Power usage is not efficient.
Q6. Mention three advantages and three disadvantages of Frequency Modulation.
Solution
Advantages:
1. In Fm receivers the noise can be reduced by increasing the frequency deviation and hence Fm reception is immune to noise as compared to AM reception,
2.Fm transmitters are highly efficient than AM transmitters as in Am transmission most of the power goes waste in the transmitted carrier.
3. FM transmission can be used for the stereo sound transmission due to a large number of side bands.
Disadvantages:
1. The bandwidth in FM transmission is 10 times as large as that needed in AM transmission.Hence wider frequency channel is required in FM transmission.
2. The area of reception for FM transmission is much smaller than that for AM transmission as the FM reception is limited to L-O-S.
3.The transmitting and receiving equipments are very complex in FM.
Q7. A modulating signal has zero dc component and peak to peak voltage of 11 V. It is used to amplitude modulate a carrier of peak voltage of 10 V. Calculate the modulation index.
Solution
Given peak voltage variation from carrier = 11 / 2 V
E c = 10 V
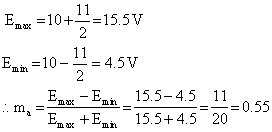
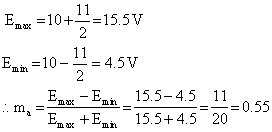
Q8. What do you mean by bandwidth of a signal? How much bandwidth is considered adequate for (i) speech signal (ii) music signal (iii) video and TV signals?
Solution
The information or message signal are also called as base band signal. In general, it spreads over a range of frequencies called the signal bandwidth.
(i) For speech signals, frequency range is from 300 Hz to 3100 Hz at the maximum end. Hence the bandwidth of speech signals = 3100 Hz - 300 Hz = 2800 Hz.
(ii) Different musical instruments produce high frequencies covering the entire range of audible frequencies from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Hence, a bandwidth of about 20 kHz is required for music signal.
(iii) Video signals require about 4.2 MHz of bandwidth. As TV signals contain both video as well as voice, hence a signal band width of 4.5 MHz is required. But to avoid interference among telecast by different TV stations, a TV channel is usually allotted 6 MHz of bandwidth for transmission.
Q9. Write the expression of a TV station, area and the population covered by the transmission.
Solution
If the height of the antenna of a TV transmitting station be h, then the range is given by
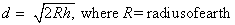 If the transmitting antenna height is h T and that of the receiver antenna is h R, then total range up to which TV programme can be received will be
If the transmitting antenna height is h T and that of the receiver antenna is h R, then total range up to which TV programme can be received will be
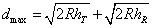 In such a case, the aerial range of TV station
In such a case, the aerial range of TV station 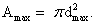 And if
And if 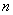 = population density,
the total population covered =Population density × area covered.
=
= population density,
the total population covered =Population density × area covered.
= 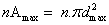
Q10. Why cannot the (i) ground waves (ii) space waves and (iii) sky waves be sustained for long distance communication beyond 10 to 20 MHz ?
What is meant by critical frequency for sky wave propagation ? Write an expression for the critical frequency in terms of the maximum electron density of the ionosphere.
Solution
The absorption of waves (loss of energy) by atmosphere increases with increasing frequency that is why ground waves, space waves and sky waves cannot be sustained for long distance communication beyond 10 to 20 MHz.
Critical Frequency : Critical frequency is the highest frequency of the radio waves which when sent normally towards a given layer of ionosphere gets reflected from ionosphere and returns to the earth.
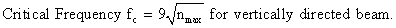 where nmax is the maximum number density of electrons in the given layer of ionosphere.
where nmax is the maximum number density of electrons in the given layer of ionosphere.
Q11. What do you mean by point to point communication and broadcast? Give examples.
Solution
In point to point communication mode, communication takes place over a link between a single transmitter and a receiver. Telephony is an example of point to point transmission.
In broadcast mode, there are a number of receivers corresponding to a single transmitter. Radio and television are examples of broadcast mode of communication.
Q12. What do you mean by analog and digital communication system?
Solution
An analog communication system is that in which the information to be transmitted is in form of a analog signal. Analog signals are continuous variation of voltage or current, generally expressed in terms of a sine or cosine functions. They are single valued functions of time. Radio broadcast and telephonic communication system are example of analog communication systems.
A digital communication system uses digital signals after properly coding them. Digital signals are those which can take only discrete stepwise values. Binary system is an example of digitalized signals. The digital communication applies coding system, which involves suitable combination of number systems.
Comments
Post a Comment