Q1. Ultraviolet light is incident on two photosensitive materials having work functions W1 and W2 (W1 > W2). In which case will kinetic energy of the emitted electron be greater ? Why ?
Solution
From Einstein"s photoelectric equation h = W + EK
EK = h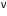 - W
Clearly, smaller the work function, greater the K.E.
As W1 > W2, K.E for metal of work function W2 will be greater.
- W
Clearly, smaller the work function, greater the K.E.
As W1 > W2, K.E for metal of work function W2 will be greater.
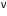 - W
Clearly, smaller the work function, greater the K.E.
As W1 > W2, K.E for metal of work function W2 will be greater.
- W
Clearly, smaller the work function, greater the K.E.
As W1 > W2, K.E for metal of work function W2 will be greater.
Q2. Show that de Broglie hypothesis of matter waves is in agreement with Bohr's theory.
Solution
According to Bohr's theory, the angular momentum of electron in a stationary orbit is equal to integral multiple of h/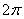 i.e.
i.e.
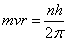 Bohr could give no reason for this quantum condition. However, de Broglie gave the reason for the same. Since electrons move in circular paths, the electron wave must be a circular standing wave that closes on itself .In other words; the circumference of the circular orbit contains a whole number of wavelengths.
Bohr could give no reason for this quantum condition. However, de Broglie gave the reason for the same. Since electrons move in circular paths, the electron wave must be a circular standing wave that closes on itself .In other words; the circumference of the circular orbit contains a whole number of wavelengths.
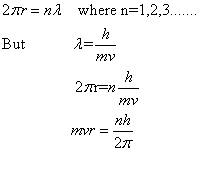
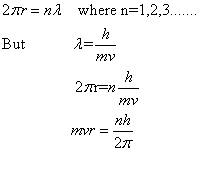
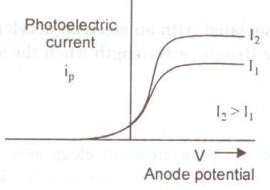
Q3. Plot a graph showing the variation of photoelectric current with anode potential for two light beams of same wavelength but different intensity.
Solution
The graph is shown in figure.

Q4. The de Broglie wavelengths, associated with a proton and a neutron, are found to be equal. Which of the two has a higher value for kinetic energy ?
Solution
De - Broglie wavelength is given by,
 Where, E is kinetic energy.
Given,
Where, E is kinetic energy.
Given,
 Now, mass of proton is slightly less than the mass of neutron.
Now, mass of proton is slightly less than the mass of neutron.
 Hence, kinetic energy of proton is slightly higher than that of neutron.
Hence, kinetic energy of proton is slightly higher than that of neutron.

 Where, E is kinetic energy.
Given,
Where, E is kinetic energy.
Given,
 Now, mass of proton is slightly less than the mass of neutron.
Now, mass of proton is slightly less than the mass of neutron.
 Hence, kinetic energy of proton is slightly higher than that of neutron.
Hence, kinetic energy of proton is slightly higher than that of neutron.

Q5. Why does photoelectric emission not take place if the frequency of incident radiation is less than threshold value?
Solution
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation,
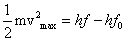 Where, m= mass of the electron
Where, m= mass of the electron
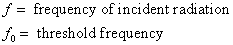 If the frequency of incident radiation is less than the threshold value (
If the frequency of incident radiation is less than the threshold value (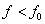 ), the K.E. of emitted electron is nagative i.e. photoelectric emission will not take place, no matter how large is the intensity of the incident radiation.
), the K.E. of emitted electron is nagative i.e. photoelectric emission will not take place, no matter how large is the intensity of the incident radiation.
Q6. Is a moving particle equivalent to a single wave?
Solution
No. A moving material particle is equivalent to a group of waves called wave packet.
Q7. The work function of cesium is 1.8 eV. Light of 5000  is incident on it. Calculate (i) Threshold wavelength (ii) Maximum K.E of emitted electrons (iii) Maximum velocity of emitted photoelectric electrons. Take h=6.63x10-34J; c=3X108m/s ; m=9X10-31Kg
is incident on it. Calculate (i) Threshold wavelength (ii) Maximum K.E of emitted electrons (iii) Maximum velocity of emitted photoelectric electrons. Take h=6.63x10-34J; c=3X108m/s ; m=9X10-31Kg
Solution

Q8. Are matter waves electromagnetic in nature?
Solution
No, they are a new kind of waves proposed to locate the position of a moving particle. For this reason, they are sometimes called pilot waves.
Q9. How do matter waves differ from a light wave as regards the velocity of the particle and the wave?
Solution
In case of matter waves, the wave velocity is different from particle velocity. But in case of light (i.e. electromagnetic wave) the particle (photon) velocity is the same as wave velocity.
Q10. Why is it difficult to remove a free electron from copper than sodium? Which has higher threshold wavelength?
Solution
The work function of copper is 4.5 eV while that for sodium is 2 eV. Therefore, radiation of more energy is required to remove a free electron from copper as compared to sodium. Since threshold radiation is inversely proportional to the work function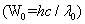 , its value will be more for sodium.
, its value will be more for sodium.
Comments
Post a Comment