Q1. The short wavelength limit of the Lyman, Paschen and Balmer series, in the hydrogen spectrum, are denoted by λL, λP and λB respectively. Arrange these wavelengths in increasing order.
Solution
λL, λB, λP
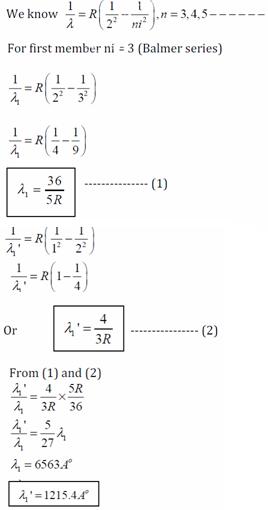
Q2. The wavelength of the first member of Balmer series in the hydrogen spectrum is 6563Ao. Calculate the wavelength of the first member of lyman series in the same spectrum.
Solution
Q3. State the limitations of Bohr's atomic model?
Solution
(1) It does not give any indication regarding the arrangement and distribution of electrons in on atom.(2) It could not account for the wave nature of electrons.
Q4. Derive the expression for the radius of the nth orbit of hydrogen atom using Bohr's postulates. Show graphically the (nature of) variation of the radius of orbit with the principal quantum number, n.
Solution

Q5. The wavelengths of some of the spectral lines obtained in hydrogen spectrum are 9546Ao, 6463Ao and 1216Ao. Which one of these wavelengths belongs to Lyman series?
Solution
1216Ao belong to Lyman series.
Comments
Post a Comment