Q1. A proton and an α particle having the same kinetic energy are in turn allowed to pas through a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the direction of motion. The ratio of the radii of their path is
Solution
Given:


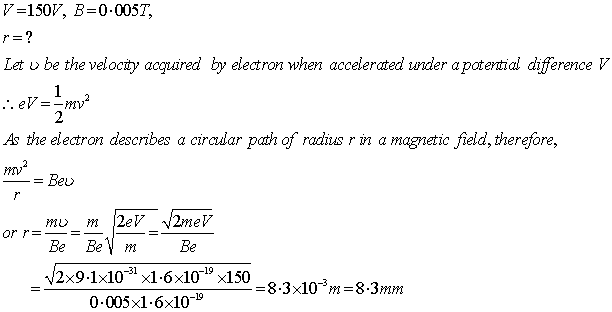
Q2. An electron after being accelerated through a potential difference of 150 V enters a uniform magnetic field of 0.0005 T perpendiculars to its direction of motion. Calculate the radius of the path described by the electron.
Solution
Here we are given,

Q3. A proton and an alpha particle enter a uniform magnetic field perpendicularly with the same speed. How many times is the time period of the alpha particle than that of the proton? Also find the ratio of the radii of the circular path of the two particles?
Solution
Time period of revolution is given as,
 Let mp = mass of the proton
mα = mass of the alpha particle.
qp = charge of the proton
qα = charge of the alpha particle.
For proton: time period,
Let mp = mass of the proton
mα = mass of the alpha particle.
qp = charge of the proton
qα = charge of the alpha particle.
For proton: time period,
 For alpha particle: time period,
For alpha particle: time period,
 =>
=> As
As  So,
So,
 Therefore,
Therefore,
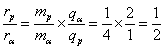 =>
=> 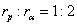
 Let mp = mass of the proton
mα = mass of the alpha particle.
qp = charge of the proton
qα = charge of the alpha particle.
For proton: time period,
Let mp = mass of the proton
mα = mass of the alpha particle.
qp = charge of the proton
qα = charge of the alpha particle.
For proton: time period,
 For alpha particle: time period,
For alpha particle: time period,
 =>
=> As
As  So,
So,
 Therefore,
Therefore,
Q4. A circular coil of 200 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.5 T, normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is 3.0 A, calculate the
(a) Total torque on the coil
(b) Total force on the coil
(c) Average force on each electron in the coil due to the magnetic field
Assume the area of cross-section of the wire to be 10-5m2 and the free electron density is 1029/m3.
Solution
Here n = 200, r = 10 cm = 0.1 m
B = 0.5 T, I = 3 A
(a) Torque is given by the relation:


 (b) The total force on a current loop placed in a magnetic field is always zero.
(c) Given N = 1029/m3, A = 10-5m2
Average force on an electron of charge (e), moving with drift velocity (Vd) in the magnetic field (B), is given by:
F = BeVd
(b) The total force on a current loop placed in a magnetic field is always zero.
(c) Given N = 1029/m3, A = 10-5m2
Average force on an electron of charge (e), moving with drift velocity (Vd) in the magnetic field (B), is given by:
F = BeVd



 (b) The total force on a current loop placed in a magnetic field is always zero.
(c) Given N = 1029/m3, A = 10-5m2
Average force on an electron of charge (e), moving with drift velocity (Vd) in the magnetic field (B), is given by:
F = BeVd
(b) The total force on a current loop placed in a magnetic field is always zero.
(c) Given N = 1029/m3, A = 10-5m2
Average force on an electron of charge (e), moving with drift velocity (Vd) in the magnetic field (B), is given by:
F = BeVd

Q5. A toroid coil has 1000 turns and diameter of 30 cm with the area of cross section of 2 cm2. Calculate i) inductance of coil ii) induced e.m.f when the a current of 2 A is reversed in 0.03 secs.
Solution
Given:
d=30 cm
r=15 cm=15×10-2 m
A=2 cm² = 2×10-4 m²
di=2 A
dt=0.03 s
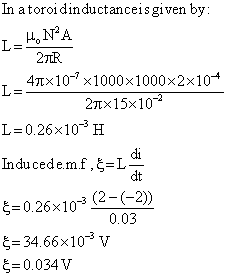
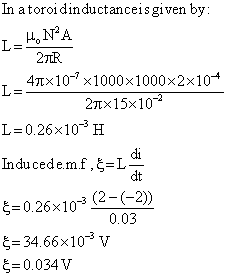
Q6. An electron beam was deflected in a given field which was perpendicular to the beam. The beam follows a parabolic path after deflection. Give answer whether the field was electric field or magnetic field.
Solution
The beam was deflected by an electric field.
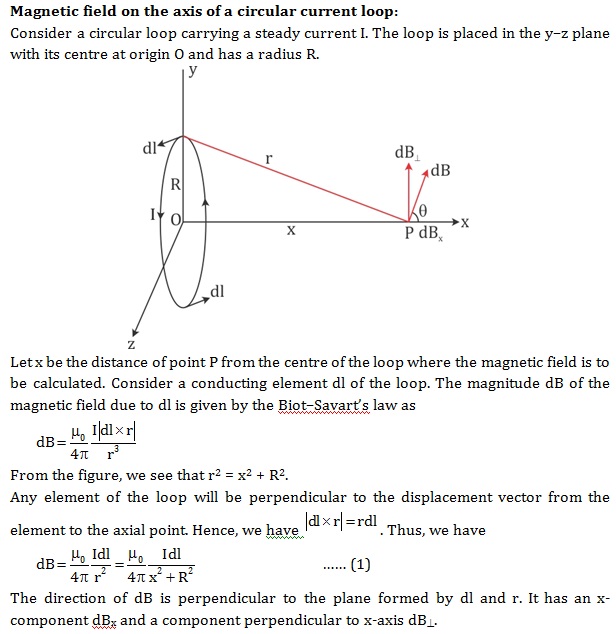
Q7. State Biot – Savart law. Deduce the expression for the magnetic field at a point on the axis of a current carrying circular loop of radius ‘R’ distant ‘x’ from the centre. Hence, write the magnetic field at the centre of a loop.
Solution


Q8. The electron in a hydrogen atom circles around the proton with a speed of 2.18 x 106 m/s in an orbit of radius 5.3 x 10 -11 m. calculate the equivalent current and magnetic field produced by proton.
Solution
v = 2.18 x 106 m/s
r = 5.3 x 10 -11 m
Time period (T)=  =
=  Equivalent current I = e/T
Equivalent current I = e/T
 Magnetic field produced by proton
Magnetic field produced by proton
 B = 12.42T
B = 12.42T
 =
=  Equivalent current I = e/T
Equivalent current I = e/T
 Magnetic field produced by proton
Magnetic field produced by proton
 B = 12.42T
B = 12.42T
Q9. The velocities of two particles A and B entering a uniform electric field are in the ratio 4:1. On entering the field they move in different circular paths. Give the ratio of the radii of curvature of the paths of the particles.
OR
You are given a low resistance R1, a high resistance R2 and a moving coil galvanometer. Suggest how would you use these to have an instrument that will be able to measure (i) current (ii) potential difference.
Solution
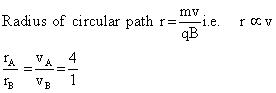 OR
(i) To measure current we shall connect low resistance R1 in parallel with the coil of moving coil galvanometer. This arrangement is called ammeter.
(ii) To measure potential difference we shall connect high resistance R2 in series with the coil of galvanometer. This arrangement is called voltmeter.
OR
(i) To measure current we shall connect low resistance R1 in parallel with the coil of moving coil galvanometer. This arrangement is called ammeter.
(ii) To measure potential difference we shall connect high resistance R2 in series with the coil of galvanometer. This arrangement is called voltmeter.
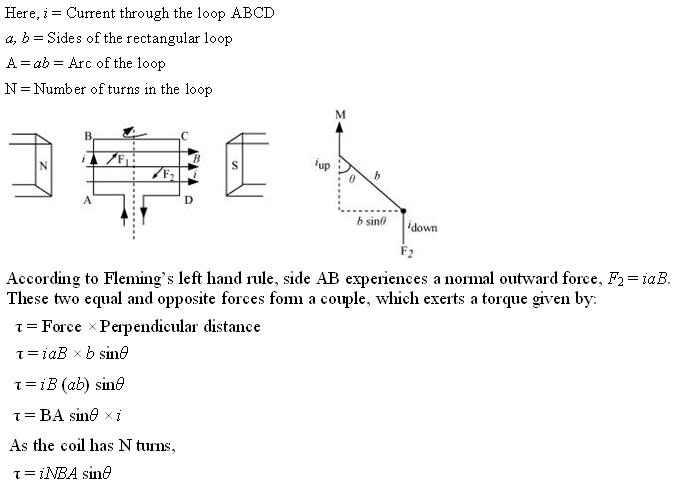
Q10. Derive an expression for the torque acting on a loop of N turns, area A, carrying current i, when held in a uniform magnetic field.
Solution
Q11. What is the length of a solenoid with total number of turns 1000, area of cross section 20 cm2 and self inductance of 4.02 × 10-3 H.
Solution
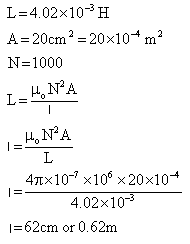
Q12. A charged particle moving in a uniform magnetic field of induction 10-3 Wb/m2 with a velocity of 106 m/s in a circular path of radius 0.45 cm. Find out the specific charge of the particle.
Solution
As we know that for circular motion of charged particle is given as,



Comments
Post a Comment